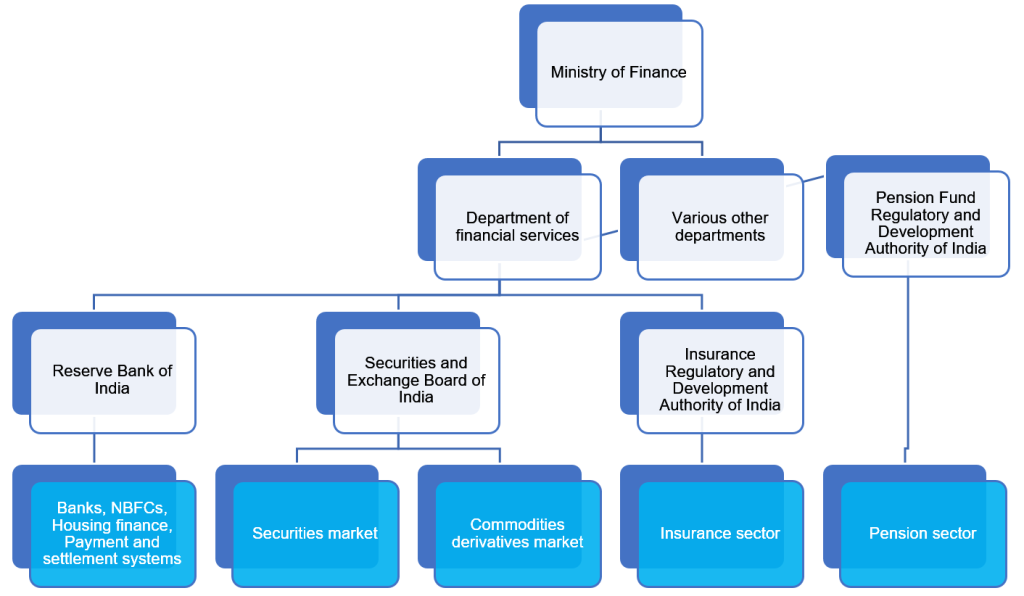
Regulated finance refers to the financial systems, institutions, and activities that operate under formal rules, supervision, and oversight set by governmental or independent regulatory bodies. These rules are created to ensure that financial markets remain stable, transparent, fair, and safe for consumers, businesses, and investors. As global economies grow more interconnected and technologically advanced, regulated finance plays an increasingly crucial role in preventing fraud, minimizing risk, and promoting long-term economic sustainability.
In simple terms, regulated finance is the backbone of a reliable financial ecosystem. Without regulation, financial markets can become dangerous spaces filled with uncertainty, manipulation, and systemic risk. With proper regulation, however, the financial world becomes a safer environment where individuals and businesses can save, borrow, invest, and transact with confidence.
Why Regulated Finance Exists
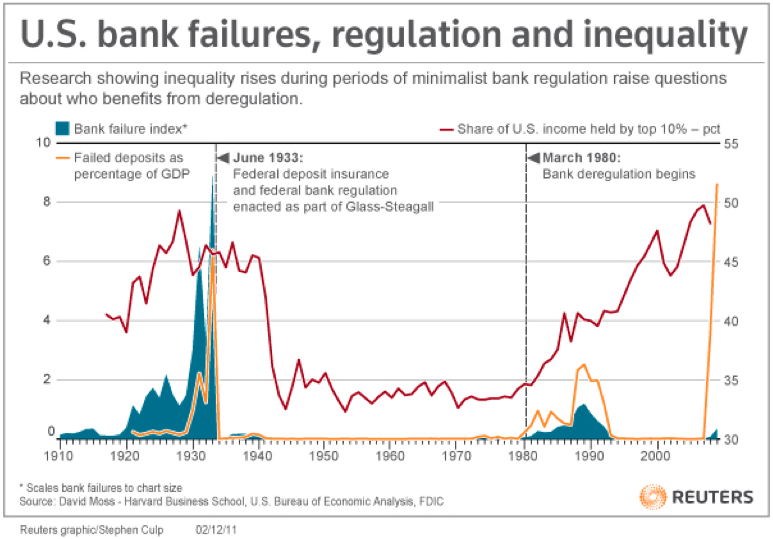
The primary purpose of regulated finance is to protect the overall financial system. Historically, financial crises have repeatedly shown that unregulated or poorly regulated markets can spiral into instability, leading to bankruptcies, unemployment, and large-scale economic downturns. When banks or financial institutions fail, the effects ripple across industries and societies. Regulation is therefore essential for several reasons:
- Protecting Consumers:
Regulations prevent banks, lenders, and financial companies from engaging in deceptive or harmful practices. This protection ensures that consumers are treated fairly, given accurate information, and shielded from predatory behavior. - Maintaining Market Stability:
Financial markets are vulnerable to speculation, risky investments, and panic. Regulation helps maintain balance, preventing sudden collapses or dangerous bubbles. - Ensuring Transparency:
Financial systems depend on trust. Regulation requires institutions to provide honest and clear information, allowing investors and customers to make informed decisions. - Preventing Systemic Risk:
A failure in one part of the system—such as a major bank collapse—can spread quickly. Regulation seeks to reduce the chances of widespread economic disruption. - Encouraging Economic Growth:
By creating a dependable financial environment, regulations help businesses access capital, investors build wealth, and societies prosper overall.
Key Components of Regulated Finance
Regulated finance includes several important components, each of which contributes to making the financial system secure and efficient. These components include:
1. Regulatory Authorities
These are the government or independent bodies responsible for overseeing financial operations. Their job is to create rules, monitor compliance, and enforce penalties for misconduct. Examples include central banks, securities regulators, and financial supervisory agencies.
2. Licensing and Registration
Financial institutions must be licensed and meet strict requirements before they can operate. This ensures that only qualified and reputable organizations participate in the financial system.
3. Capital Requirements
Regulators often require banks to maintain a minimum amount of capital. This ensures they can absorb losses and protect customer deposits during economic stress.
4. Compliance Rules
Financial institutions must follow certain rules related to risk management, reporting, privacy, and ethical behavior. Regular audits and inspections maintain accountability.
5. Consumer Protection Policies
These include rules about how financial products must be advertised, how interest rates are explained, and how disputes are handled. They empower consumers and ensure fairness.
Regulated Finance vs. Unregulated Finance
Understanding the difference between regulated and unregulated finance helps highlight why regulation is so vital.
Regulated Finance
- Operates under strict legal oversight
- Requires financial transparency
- Protects customers through safety measures
- Encourages long-term economic stability
- Holds institutions accountable
Unregulated Finance
- Operates with little or no oversight
- Higher risk of fraud or market manipulation
- Increased possibility of financial crises
- Lack of consumer protection
- Often linked to illegal or unethical activity
While unregulated finance may offer short-term opportunities or fast profits, it poses significant long-term risks. Regulated finance, on the other hand, prioritizes stability and trust.
Benefits of Regulated Finance
A well-regulated financial system brings many advantages to society:
1. Trust and Confidence
When people trust the financial system, they are more likely to save, invest, and borrow responsibly. This trust strengthens the entire economy.
2. Reduced Fraud and Crime
Regulations help detect and prevent fraud, money laundering, and financial crimes. Transparency keeps criminals from exploiting the system.
3. Protection During Crises
Regulated institutions are often required to hold emergency reserves and follow risk-management guidelines. These measures help them survive during economic downturns.
4. Fair Competition
Regulation prevents large institutions from abusing their power. It ensures that all players—big and small—follow the same rules.
5. Economic Growth and Stability
Stable financial systems attract foreign investment, support entrepreneurship, and create jobs.
The Role of Technology in Regulated Finance
As technology transforms banking and finance, regulation has had to evolve as well. Modern regulated finance now includes oversight of:
1. Digital Banking
Online banking platforms must follow the same rules as traditional banks while also ensuring cybersecurity and data privacy.
2. Fintech Innovation
Payment apps, digital wallets, robo-advisors, and online investment platforms must meet regulatory standards to protect users.
3. Cryptocurrencies
Although many cryptocurrencies operate outside traditional regulation, governments worldwide are now developing rules to manage digital assets, prevent scams, and protect investors.
4. AI and Algorithmic Trading
Automated financial systems must be monitored to ensure they do not create risks or unfair advantages in the market.
Technology brings convenience and innovation, but it also increases complexity. Therefore, the role of regulation continues to grow.
Challenges Facing Regulated Finance
Despite its importance, regulated finance faces several challenges:
1. Rapid Technological Change
Regulators must keep up with innovation to ensure safety without slowing progress.
2. Globalization
Financial activity often crosses national borders, making regulation more complex.
3. Balancing Control and Freedom
Too much regulation can limit business growth, while too little can lead to instability. Achieving balance is a constant challenge.
4. Cybersecurity Threats
Hackers and cybercriminals pose serious risks to financial institutions. Regulation must evolve to address these digital threats.
Why Regulated Finance Matters for the Future
As financial systems become more global and digital, the role of regulated finance becomes even more essential. It ensures that new innovations are introduced safely, consumers remain protected, and economies stay resilient in the face of change.
Regulated finance represents a promise: a promise that financial markets will remain secure, transparent, and fair for everyone. Whether someone is opening a bank account, investing in the stock market, taking a loan, or starting a business, regulated finance provides the stability they need to move forward with confidence.
In the future, regulated finance will continue to evolve with technology, global trade, and consumer demands. Strong regulation helps build a world where opportunity is available to all, risk is managed responsibly, and financial progress benefits society as a whole.